Category: Blog

3 Nov Preparing for AI in Manufacturing: Get Your Data House in Order
The changeover took 3 hours instead of 45 minutes, and nobody knows why. Can AI help? Not yet. AI cannot fix broken data, and it cannot analyze data that was never captured. Real wins come from capturing the right signals, making them consistent, and connecting them with context.
The Digitization Imperative
You’ve heard the buzz: manufacturers using AI are pulling ahead while others fall behind. McKinsey reports that digital leaders in manufacturing see 30-50% reductions in machine downtime and 10-20% increases in throughput. But here’s what the consultants won’t tell you: these wins don’t come from AI alone. They come from finally capturing and connecting the data that’s been invisible on your plant floor for years.
The gap between leaders and laggards is widening. Not because of AI magic, but because leaders digitized their operations first. They can see what’s happening, when it’s happening, and why it’s happening. Everyone else is still guessing.
Can AI Fix Your Data Problems?
Short answer: no.
AI can find patterns, but it cannot repair systemic problems like:
- Inconsistent naming (is it “changeover,” “setup,” or “product change”?)
- Missing links between systems (which tool was running when quality spiked?)
- Unsynchronized clocks (did the defect happen before or after the parameter change?)
- Signals that were never captured (nobody tracks individual changeover tasks)
For example, if you don’t track changeover tasks, tool IDs, or first-piece checks, no model can analyze or optimize them. At best, you get superficial correlations. At worst, you automate bad decisions.
The 6 Cs: What Your Data Must Have Before AI Can Help
AI needs 6 foundational elements to deliver value:
- Coverage: The signals exist for the process you want to improve. Examples: machine states, setup times, changeover tasks, rejects, first-piece checks, maintenance work.
- Consistency: Names, codes, and units mean the same thing everywhere. “Changeover” is not split across three different abbreviations.
- Context: Events link across systems and time. A reject on Line 2 ties to product, lot, tooling, shift, and the exact recipe or program version.
- Currency: Data reflects the current state. No working with yesterday’s numbers when today’s are available.
- Cadence: Data flows from event to system fast enough to act
- Credibility: People trust the numbers because they are complete, validated, and auditable.
What Goes Wrong Without These
You may be able to run your plant without these all at a high level of maturity but there are some downsides:
- Machine blindness: You know changeover takes 3 hours but not why. After adding task-level tracking, one plant discovered 40% was waiting for QC approval … not actual setup work.
- Tower of Babel: Three shifts log the same problem as “material issue,” “stock-out,” and “waiting for parts.” Management spends months fixing the wrong bottleneck until someone standardizes the codes.
- Mystery failures: Scrap doubles every Tuesday afternoon. Six months of head-scratching until someone finally connects it to Monday’s raw material delivery from a specific supplier.
- Yesterday’s news: Line switched to Product B two hours ago, but inventory system still allocating materials for Product A. Expedites and chaos ensue.
- After-the-fact alerts: Operator notices quality drift at 2 PM. Alert hits the engineer’s screen at 2:20 PM. By then, 300 units are scrap.
- Fantasy metrics: Dashboard shows 92% OEE. Operators know it’s closer to 70% because breaks aren’t logged and micro-stops under 3 minutes don’t count. Management celebrates the “good performance.”
Changeover Could Be a Great Starting Point
Changeover is the end-to-end set of tasks to switch products: de-stock, clean or sanitize, swap tooling, load recipe or program, first-piece check, ramp. While flow is the smooth movement of work with minimal stops, microstops, and rework across the line.
Why start here? Changeovers are frequent and measurable, and they force good data hygiene. Timestamp each task, standardize reason codes, and connect events to product, lot, line, shift, and version. You usually unlock net capacity quickly while building the same data foundation that later powers quality and maintenance use cases.
A Practical Digital Maturity Ladder
Every organization is at a different maturity level, if you find yourself at Level 0 or Level 1 it would be a good idea to evaluate if there are some digitization options that could get you started in the near future.
Level 0 – Paper: Whiteboards, tribal knowledge, spreadsheets
Level 1 – Digital Islands: Systems exist but don’t connect
Level 2 – Connected Operations: MES ties everything together with context
Level 3 – Trusted Intelligence: Governed data, validated entries, role-based views
Level 4 – Optimizing System: Metrics trigger actions, results feed improvements
Most plants can reach Level 2 in 90 days with focused scope.
Where AI and analytics pay off first
- Changeover time reduction: Identify the longest tasks, sequence them better, pre-stage materials and tools, and standardize best practice. Small savings per change add up to real capacity.
- Downtime and microstop patterns: Cluster similar stops to target the true top loss. Many plants win here before moving to heavier predictive work.
- Quality drift alerts: Start simple with rule-based thresholds tied to process context. Move to predictive models once false alarms are low.
- Maintenance prioritization: Combine run conditions, fault history, and criticality to rank what to fix next.
- Schedule optimization: Use actual setup times and changeover data to plan sequences that minimize total loss.
Metrics That Show You’re Ready
- Being able to quickly track these metrics isn’t optional, it’s the foundation for unlocking AI value.
- Critical equipment with state tracking: >90%
- Downtime/rejects with standard codes: >95%
- Events linked to full context: >80%
- Event to dashboard time: <5 minutes
- Data quality score: >85%
- Changeover variance by product: <10%
How Atachi Helps
Atachi specializes in rapidly connecting your manufacturing data islands. We typically:
- First 30 days: Connect machine states and operator inputs with full context, standardize code lists
- By 90 days: Link MES, QMS, CMMS, and ERP across your systems
- By Month 4: Deploy role-based dashboards operators actually trust
Once your data foundation is solid, AI becomes a plug-and-play addition rather than a science project.
Take Action Now
You do not need millions or a two-year roadmap. Start on one line, prove value in 90 days, and build momentum.
AI rewards plants that measure the right things the same way every day. Build coverage, consistency, context, currency, cadence, and credibility. Start with changeovers and flow, then expand with confidence.
When will you start?

21 Jun Benefits Of QMS to Improve a Company’s Processes
Use your QMS to keep your company’s policies and procedures aligned with the launching and scaling of your products.
The digital age has changed the way we act, think and communicate. Yet, in so many cases the world of quality and compliance is still managed and indeed hampered by manual, paper-based systems. Quality management needs to move into the digital age. By modernizing legacy processes with an Electronic Quality Management System (eQMS) organizations can meet today’s quality challenges.
Quality Management Systems (QMS): Enable manufacturers to electronically monitor, manage and document their quality processes to help ensure that products are manufactured within tolerance, comply with all applicable standards and do not contain defects.
Quality Management System (QMS) software:
- Provides the procedures, processes, structure, and resources needed to streamline manufacturing and ERP operations while cost-effectively managing quality issues.
- As part of a closed-loop quality process proactively monitoring events across any enterprise source, effectively integrated Quality Management Systems (QMS) can identify potential problems before quality issues occur.
- Events may include supplier issues, manufacturing non conformances, complaints, services, and audits – both local and global.
- Provides the procedures, processes, structure, and resources needed to streamline manufacturing and ERP operations while cost-effectively managing quality issues.
- As part of a closed-loop quality process proactively monitoring events across any enterprise source, effectively integrated Quality Management Systems (QMS) can identify potential problems before quality issues occur.
- Events may include supplier issues, manufacturing non conformances, complaints, services, and audits – both local and global.
Benefits Of Quality Management Systems:
Implementing a quality management system affects every aspect of an organization’s performance.
Quality Management Systems (QMS) integrated with Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) are strategic to a manufacturer’s business, providing complete visibility to manufacturing, field use and service information.
This knowledge helps to improve future product design efforts and to optimize production methods, allowing quicker ramp up in manufacturing.
As a result, manufacturers employing integrated Quality Management Systems (QMS) enjoy
- Decreased time to market,
- Real-time product risk evaluation,
- Minimization of recalls and negative brand exposure, and
- Lower per-product costs due to quality and process improvements as well as
- Decreased waste.
Additional benefits:
- Dramatic reduction of internal and external quality incidents
- Consistently higher-quality product output
- Significant reduction in the cost of quality operations
- A shift from problem detection to problem prevention
- Streamlined compliance with corporate and industry regulations
These benefits offer additional advantages, including:
- Defining, improving, and controlling processes
- Reducing waste
- Facilitating and identifying training opportunities
- Engaging staff
- Setting organization-wide direction
- Communicating a readiness to produce consistent results
Quality Management Systems (QMS) Capabilities and Outcomes:
Capabilities offered by Quality Management Systems (QMS) include:
- Global visibility across distributed operations
- Enforcement of process to ensure compliance
- Event monitoring and early trend escalation
- Global risk management
- Automatic containment of suspect items
- Intelligent root-cause analysis
- Automated quality assurance
- Adaptable best practices
- Enterprise scalability
How do different business functions benefit from using QMS?
While the importance of QMS has traditionally been as a quality, audit and risk tool, some of the biggest gains come in other areas, such as leadership, customer service, sales and marketing, procurement, and HR. This has led to many organizations dropping the word ‘quality’ from ‘QMS’ and rebranding it as the business management system.
Element And Requirements Of A QMS:
Each element of a quality management system helps achieve the overall goals of meeting the customers’ and organization’s requirements. Quality management systems should address an organization’s unique needs; however, the elements all systems have in common include:
- The organization’s quality policy and quality objectives
- Quality manual
- Procedures, instructions, and records
- Data management
- Internal processes
- Customer satisfaction from product quality
- Improvement opportunities
- Quality analysis
Establishing And Implementing A QMS:
Before establishing a quality management system, your organization must identify and manage various connected, multi-functional processes to help ensure customer satisfaction. The QMS design should be influenced by the organization’s varying objectives, needs, and products and services provided. This structure is based largely on the plan-do-check-act (PDCA) cycle and allows for continuous improvement to both the product and the QMS. The basic steps to implementing a quality management system are as follows:
- Design
- Build
- Deploy
- Control
- Measure
- Review
- Improve
Meeting the customer’s requirements, which helps to instill confidence in the organization, in turn leading to more customers, more sales, and more repeat business
Meeting the organization’s requirements, which ensures compliance with regulations and provision of products and services in the most cost- and resource-efficient manner, creating room for expansion, growth, and profit
The purpose of QMS is to ensure that, every time a process is performed, the same information, methods, skills and controls are used and applied in a consistent manner.
A QMS organizes this information to give each person access to their own custom to-do list. Permissions control who sees what and when. Overall, a QMS delivers a complete record of business processes, so you can better understand improvement initiatives.
Atachi QMS has an in built intelligence to capture documents processes, procedures, and responsibilities for achieving quality policies with strict adherence to GMP (Good Manufacturing Practices) and objectives of an organization.To learn more about Atachi QMS click here.

14 Jun How We Can Use Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Software?
Continuous Change Requires Continuous Innovation:
Today’s pharmaceutical manufacturers and distributors are witnessing a paradigm shift in consumer behavior, market dynamics, margins, and increased compliance mandates brought about by the influx of modern technology.
- Efficient business processes,
- Centralized management,
- Quick decision-making, and
- Clear analytics
have become essential for any business to grow in the modern-day scenario.
What is pharmaceutical manufacturing technology?
The Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Technology (PMT) program is a specialized chemical technology program designed to meet the needs of the pharmaceutical and related industries (cosmetics, food, plastics, custom chemicals, research centers, pilot plants, etc.)
What do pharmaceutical manufacturers do?
Pharmaceutical manufacturers manage the distribution of drug products from the point of production to the drug wholesalers and in some instances, directly to retail pharmacy chains, specialty pharmacies, hospital chains as well as some health plans.
Manufacturers in the Pharma industry are challenged with a variety of regulatory compliance and government-mandated requirements that add cost and risk to their business. They must maintain strict quality management and detailed product documentation to meet customer specifications and regulatory requirements.
What Is Pharmaceutical Software?
Pharmaceutical manufacturing software refers to an umbrella term for a variety of technology solutions used by manufacturers, raw material suppliers, and wholesalers, including drug stores and healthcare provider
Tight healthcare budgets and long product development Lifecycle makes it difficult for a pharmaceutical business to maintain a competitive edge. It is designed to handle all of the pharmaceutical industry’s unique manufacturing, distribution, and accounting needs.
What is ERP in pharma?
An ERP software for pharma manufacturing industry not only enables the consolidation and integration of pharmaceutical manufacturing processes across multiple units but also helps businesses to keep a track of sensitive operations across the organization, such as compliance, expiry management, quality, formulation, and costing, etc.
Modern ERP with embedded AI, automation, and an immersive user experience is enabling continuous innovation across the business.
Benefits of ERP Software in Pharmaceutical Manufacturing:
Pharmaceutical ERP software offers the following benefits:
- ERP systems for pharmaceutical manufacturing ensure absolute compliance with the stringent regulations
- Eliminate risk by delivering safer products of superior quality at the right price and right time
- Introduce new products to market faster and cheaper than competitors
- Real-time batch monitoring to make perfect business decisions
- ERP software for the Pharmaceutical Industry helps in maintaining formula secrecy
- Respond quickly to customer demands
- Smoothen operational process flow and enhance profits
- Enhance the quality, consistency, and speed to deliver drugs to market
- Control costs through reduced wastage, optimum material utilization, and inventory management
- Pharma ERP software offer end-to-end bi-directional traceability, from the raw material to the finished product
The selection criteria for an ERP system:
“Which ERP software will meet our business requirements?”
- Your current software doesn’t meet your business needs
- Your competitors are getting ahead of you
- You’re wasting time manually tracking and monitoring inventory manually
- Your employees don’t like the software and complain regularly
- You spend a lot to keep the software updated
- You have disorganized data, and it’s hard to get the information needed quickly
Always remember your business goals while selecting ERP software. Here are some elements to keep in mind while going through the ERP selection process.
- Business requirements
- Management support
- User support
- Budget and resources
- Technology and future scalability
- Necessary customization
- Integration with existing systems
While selecting and evaluating ERP solutions, manufacturers should talk about the
- Industry-specific functionality offered,
- Future readiness of the software,
- If the software integrates with and supports digital capabilities, and
- What are your expectations for vendors?
A strong and experienced ERP partner can help you maximize your Return on Investment (ROI).
The implementation team takes the time to understand your specific requirements and recommends the right tool or solution that will complement your business needs.
When you evaluate multiple ERP options,
- Ask about functionalities,
- Ease of use,
- If the software is compatible with developing technologies,
- What the total cost of ownership is? and
- What training is available for users?
Here are some key questions to ask ERP providers in the selection process.
- What modules do they provide?
- Do they support advanced technologies?
- Do they offer a manufacturing-specific solution?
- Is their solution customizable and can it integrate with other tools?
- Are there limitations on the number of users?
- What kinds of software support do they offer?
- What is their industry experience?
Clearly defining your selection criteria for an ERP system while embarking on your research can help ensure good communications with vendors about their software. Make sure you understand all aspects of each solution to avoid regrets later.
ERP for Pharmaceutical Distributors:
A pharmaceutical distributor, while still operating under state legislation, will not be as closely regulated as manufacturers and as there are plenty of solutions that will let you create a manufacturing record and trace product genealogy you will have a bit more room to choose the best solution for you. This means that we can now look at more agile and cloud-based ERP products, such as Dynamic365.
As the markets continue to shrink, ERP software for pharma manufacturing industry has become an essential component of business management. Faced with global competition, pharma companies need to re-engineer their processes frequently to match up and maintain their quality. Adapting a comprehensive ERP software for pharma is a key step towards scaling and growing businesses in this segment.
Stay ahead of problems and take advantage of trends through machine learning prediction, intelligent automation, and other technologies.

14 Jun MES vs. ERP: ‘How to’ vs. ‘Why’
ERP knows the ‘why’ of things, MES knows the ‘how to’.
While MES Sofware solutions primarily support business decisions, the ERP supports the operational ones.
Features of MES software solution:
- Collect process and machine data from data silos
- Automatically create notifications and logs for issues
- Enforce product specifications and business rules
- Defect tracking and automated corrective actions
- Perform real-time quality checks and yield monitoring
- WIP tracking and genealogy management (order, lot, product)
Features of ERP systems:
- Integration – A central view of essential financial, operational and business data that can be shared across the organization in near-real-time.
- Automation – ERP provides the ability to automate repeatable business tasks, such as payroll, order processing, invoicing, reporting and more.
- Data Analysis – Enabling employees to gather a wide variety of information and spin it into actionable insights
- Reporting – Compile information about business operations into reports that empower stakeholders to make more informed decisions, enhance business processes and identify problem areas before the business suffers.
- Tracking and Visibility – Allow companies to track, surface and understand business metrics
- Accounting- Ability to track, store and analyze financial data, such as accounts payable (AP), accounts receivable (AR), general ledger (GL), budgets and forecasting.
- Financial Management – Assist finance teams with the management process by tracking, analyzing and reporting critical business data.
- CRM- Bring customer relationship data into the mix, expanding the view of the business
- Sales and Marketing – Benefit marketing and sales teams by making it easier for them to sell, upsell, generate quotes and purchase orders, forecast, manage commissions and track key details like profit margins and ratios
- Human Resources – Acts as an end-to-end employee management platform, handling payroll, hiring, onboarding, compensation management and timekeeping.
- Supply Chain Management – Offer insight into a company’s supply chain management (SCM) efficiency by tracking demand, inventory, manufacturing processes, logistics and distribution.
- Manufacturing – Create efficiency in manufacturing processes by assisting with product planning, sourcing raw materials, production monitoring and forecasting.
What are the main goals of MES software?
- Improve quality while driving down production costs
- Improve the efficiency and throughput of production
- Enable a paperless workflow and eradicate errors
- Meet complex regulatory and client requirements
- Reduce lead times and improve delivery reliability
- Enhance inventory velocity and flow of materials
What are the main goals of ERP software?
- Improve customer service and data management
- Enhance inventory & supplier management
- Support advanced real-time planning
- Streamline communication & collaboration
- Enable more informed management decisions
- Synchronize reporting across departments
Who uses MES software?
An MES platform is mainly used by people who are involved in production, going from plant managers to process engineers and operators.
ERP software is used on a daily basis by:
- The sales department to enter and track production orders
- Supply chain managers to schedule production orders
- Inventory & procurement to order new raw materials on time
- The HR department for payroll management and administration
- Finance teams & CEOs for business analysis and forecasting
- The marketing team for pre-sales activities and sales follow-up
Difference between ERP & MES software:
ERP software focuses on integrating business processes and synchronizing reporting across departments. Data is displayed over a period of time, often with a certain latency. ERP is mostly used by people in business outfits and requires some training in order to make it your own.
MES software lands on the other side of the moon. It is used on the factory floor and focuses on optimizing the manufacturing process itself. MES provides visibility, information and detailed metrics of manufacturing operations in real-time, simplifying the workflow of machine operators. Take a look at following difference between MES and ERP.
| ERP | MES |
| Business intelligence & reporting | Track & trace products & batches |
| Order processing & fulfillment | Guide the workflow of operators |
| Inventory management | Real-time production monitoring |
| Customer relation management | Automated waste registration |
| Supply chain management | Analyze production bottlenecks |
| Customer management | Finding reasons for downtime |
| Human resources management | Product quality optimisation |
| Marketing & sales | Schedule specific products |
Wrapping It All Up : MES VS ERP
So the difference between an ERP and an MES and what they do best is:
ERP is the financial information system for the company.
MES is focused on the building of the Products that the company produces.
MES & ERP: A Match Made in Heaven:
ERP and MES solutions have a lot of crossovers between them in how they track the production process. However, manufacturing companies in Industry 4.0 need a blend of the two systems to make the plant run at its maximum performance and present accurate information for decision-makers.When ERP and MES systems are integrated, data from management functions such as customer service, order processing, finance and purchasing are integrated with data from manufacturing, such as production scheduling, machine throughput, WIP, inventory changes, shipped orders, and quality management. This results in gate to gate traceability and transparency to real time changes that current disparate processes could not capture.
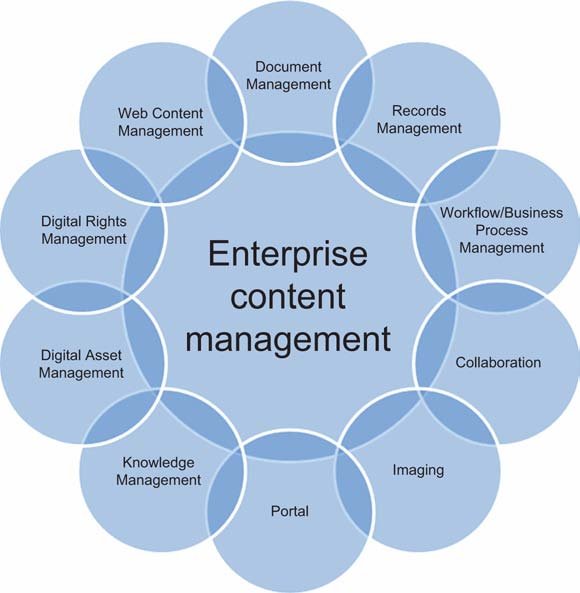
25 Nov What is Enterprise content management (ECM)?
Want to Make Decisions, Complete Projects, and work with Maximum Efficiency? – The Right ECM System will help you.
It is a systematic approach to managing content throughout its lifecycle. It enables unstructured information — such as Word documents, PDFs, emails, and scanned images — to be securely stored and made accessible to authorized users. By eliminating dependence on paper documents and organizing unstructured information according to business needs, organizations can simplify and streamline work.
How is ECM defined?
It is a set of defined processes, strategies, and tools that allows a business to effectively obtain, organize, store and deliver critical information to its employees, business stakeholders, and customers.
Enterprise Content Management Software:
Enterprise content management software provides corporations and organizations with a central repository to store, manage, archive, and otherwise handle data of varying degrees of confidentiality and importance.
Key Benefits of (ECM) Software.
- Connect, access, visualize, maintain, manage, and eliminate siloed content repositories with a single overarching architecture.
- Increase employee productivity and reduce file redundancy.
- Automate business processes, making them structured, documented, and auditable.
- Ensure government compliance through strict maintenance of file security, permissions, approvals, and lifecycle.
- Integrate with other types of content management software to provide all-encompassing enterprise content management services.
- Simplify workflow and Centralize collateral in one repository.
Who Uses (ECM) Software?
The benefits of enterprise content management software are not limited to one specific company size or sector.The solutions offered can be helpful to any company that requires better organizational tactics, whether that is in regards to their HR department, finances, account management, sales and marketing, administration, planning, governance, or another area.
Enterprise Document Management System– Document management, often referred to as Document Management Systems (DMS), is the use of a computer system and software to store, manage and track electronic documents and electronic images of paper-based information captured through the use of a document scanner. A document management system is used to automatically organize, secure, digitize and classify company documents, making them easy to access, edit and share.
Document management system software:Now, we can define document management as the software that controls and organizes documents throughout an organization. It incorporates document and content capture, workflow, document repositories, COLD/ERM, and output systems, and information retrieval systems. Also, the processes used to track, store, and control documents.
What Key Features Should a Document Management System Have?
A document management system should have the following features:
- Powerful Workflows
- Data Integration
- Report Management
- Advanced Security Features
What are the Benefits of a Document Management System?
Document management systems should improve the way things run at your organization. They should give you:
- More Time to Do the Work That Matters
- Convenience for an Increasingly Mobile Workforce
- Peace of Mind.
Your business is growing and so are your documents. Shouldn’t you be growing along with it? A document management system can take the burden of mundane tasks off your plate. That means more meaningful work—and more opportunities to grow your career alongside your organization.
10 Mar What is MES Software? Some Important Benefits and Details
What Is MES Software? Some Important Benefits and Details
The Hidden Factory – Not To Be Ignored:
The Hidden Factory refers to parts of a manufacturing process that decrease the quality or efficiency of operation -the mistakes, the rework, the waste – all the things that are kept hidden from the eyes of the customer. It is called the “hidden factory,” and it causes unseen profit leaks to companies every day of every year.
- These wasteful processes and work go unreported and undocumented and are dangerous to a company’s bottom line.
- These factories are fueled by a dangerous attitude that the headaches and heartache caused by this Hidden Factory are surely worth it if the customer remains unaware and is ultimately happy with the product.
- All too often these daily drains on resources are going unnoticed or are even accepted as part of the process itself.
Of course, you care about lost time, money, and effort, but how are you supposed to correct something you can’t see?
MES- How It Exposes The Hidden Factory:
A modern Manufacturing Execution System (MES) captures data that can be analyzed to uncover flawed processes, providing insights that expose the hidden factory.
How?
- A flexible MES documents, tracks, and reports the time it takes to deal with events When studied with a trained eye, these reports reveal what went right and what went wrong.
- Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) deliver a number of long and short-term manufacturing benefits, as well as strategic benefits such as improved yields, lowering operating costs, and increased compliance.
What is MES?
According to MESA (Manufacturing Execution System Association International),
- Manufacturing execution systems deliver information that enables the optimization of production activities from order launch to finished goods.
- Using current and accurate data, MES guides, initiates, responds to, and reports on plant activities as they occur.
- The resulting rapid response to changing conditions, coupled with a focus on reducing non-value-added activities, drives effective plant operations and processes.
- MES provides mission-critical information about production activities across the enterprise and supply chain via bidirectional communications.”
- Manufacturing Execution Systems collect multiple plants’ production information and integrate easily with equipment, controllers, and enterprise business applications.
- Although MES solutions are used to operate as a self-contained system, they are increasingly being integrated with enterprise resource planning (ERP) software.
- The result is complete visibility, control, and manufacturing optimization – from the order placing, production inception, and process control to product output.
Why Do Companies Need A Manufacturing Execution System?
- Many companies still enter data manually or share work instructions on paper. Most of them, however, know there is a better way to organize the mass of activity happening on the plant floor.
- MES provides visibility to that activity as well as the underlying data, uses that data to improve how that activity is done and makes it repeatable.
- It connects multiple sites, integrates with equipment, and raises the effectiveness of business applications all to better optimize operations.
- MES technology is helping manufacturers to reduce cycle times and achieve cost savings (production does not continue when critical issues are encountered), whereas the opportunity to improve planning activities is also resulting in improved utilization of equipment.
- These systems also automate many manual documentation tasks, thereby eliminating related deviations and achieving better compliance. They are also removing calculation and review tasks that ordinarily would require considerable manual effort.
How does the move towards web-based MES solutions making it easier to support production operations and real-time activities:
- HTML5 support now enables organizations to access MES across a range of digital devices, including tablets and smartphones, with ease.
- This makes it a lot easier to migrate manual processes to the electronic world as the need to deploy expensive infrastructures no longer exists; all is needed is a wireless network, which is often already in place.
- The device proliferation also simplifies real-time involvement in the process, making all parties aware of what is happening at any given time.
- Although planning needs to remain a cornerstone of GMP, being aware of issues as they occur provides a level of understanding that often cannot be achieved after the fact, thus leading to better decision making.
- Although some manufacturers are still wary about the associated challenges that go together with implementing a new system, breaking the project down into phases, starting with the functionality that will provide the biggest return, can make the whole process much more approachable.
- Indeed, once the organization has created a success story and brought all its stakeholders on board, it’s easier to define the scope of the remaining areas.
The 3 Pillars of an MES:
-
Establishing a plan and staying on schedule
The system takes your input – production shifts/times, production goals, etc. and calculates your TAKT time. Operators see real-time progress on dashboard graphics, knowing the progress at every moment.
-
Enforcing a repeatable process
Knowing your process is being followed exactly as defined provides the ultimate peace of mind. Every step, from fastening to product routing, is nailed just as you defined it time after time.
-
Creating a rich data set:
Capturing data is one thing; being able to act on that data is really the key to driving improvement initiatives. Use your business intelligence platform, explore your data set, and identify and solve your hidden inefficiencies.
All three of these MES pillars are used to help you reach productivity and quality goals by:
- Solving production scheduling challenges
- Discovering and sharing your best operators’ insights
- Uncovering inefficiencies in your process and fixing them
- Reducing the exhausting task of putting out fires
- Establishing a continuous improvement philosophy
- Increasing operator engagement and dedication
MES Is For All Industries:
- Manufacturing execution systems (MES) are being used across industries, and are seen in a number of the discrete, batch, and continuous process manufacturing industries including semiconductor, aerospace, metals, plastics electronics, medical devices, automotive, pharmaceuticals, glass, and more.
- A Manufacturing Execution System (MES) with a configurable platform adapts to the users’ business without custom code, and has an open SOA architecture designed for ease of integration to enterprise applications and shop floor automation.
But Why Should Pharma And Biotech Companies Use An MES?
What is MES in pharma?
- Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) enable pharmaceutical manufacturers to improve performance and reduce operational cost, while simultaneously increasing compliance with regulatory requirements.
- MES digitizes your pharma and biotech production. In today’s intense economic conditions, spiraling overheads are compelling manufacturers to optimize their production processes, leading to a demand for new approaches that can improve efficiency and better utilize expensive resources.
- As the industry evolves and the complexity of managing drug manufacturing programs increases, MES technology has also advanced at considerable speed and come a long way in terms of functionality and flexibility.
- MES solutions enable manufacturers to plan, direct, track and analyze every stage of their operations.
- Today, these systems provide real-time management capabilities, full support to replace paper documents with electronic documentation (electronic batch records [EBRs] and electronic logbooks [eLogbooks]), and seamless integration with enterprise resource planning (ERP) and automation systems.
- They also offer compatibility with multiple plug-in applications, meaning they can accommodate the most complex workflows into their design while contributing new levels of adaptability through modularity and off-the-shelf configuration.
- MES technology is equipping manufacturers with comprehensive data to help with proper recipe management and electronic batch processing recording, reducing the risk of production issues and, most importantly, improving product quality. And they are an important prerequisite for digitization and Pharma 4.0.
- At the highest level, MES needs integration between the ERP and shop floor automation.
What Is The MES System In SAP?
- SAP maintains the record of materials, BOM, routings, and orders; the MES maintains the records/transactions such as WIP (work in progress).
- For implementing the MES, the consultant has to perform a detailed analysis of MES requirements such that they can be mapped with the manufacturing environment.
- The consultant has to perform the analysis of the integration with SAP PP since there is an overlap of functionality offered by SAP and MES software
Companies like Atachi Systems have worked with several top global pharma manufacturing companies who have used the other MES platforms and struggled to get the value out of these MES platforms; hence we call them legacy platforms.
- Atachi NGIMES platform has eliminated all the pain points that companies are struggling with legacy platforms.
- Their platform is the only MES solution entirely built on the SAP HANA platform that leverages Big Data analytics and AI, which need tomorrow’s business.
Because of these reasons, Atachi systems have been listed as TOP Global MES platforms by several research firms in the last few years, repeatedly.
What are Atachi solutions offerings for Pharma 4.0?
- They are helping the pharma manufacturers to get them on to the Pharma 4.0 journey and realize complete business agility (quickly and cost-effectively) for their customers with real-time insights.
- As part of their platform, they offer EBMR, logbooks, DMS, CAPA, IIOT, TMS, Supplier quality management, Real-time analytics, Mobility, big data, and AI at a single license cost.
- Users don’t need to pay separately for each functionality; everything comes as a single package in a USE-AS-NEEDED approach.
MES is a Holistic Solution:
MES isn’t a stop-gap, quick-fix, or miracle solution (although it can seem magical at times). It’s really a system for digitally transforming your entire facility’s manufacturing execution.
You need to explore how an MES implementation will influence your established processes and how those processes may change. That requires upfront thought about change management within your organization. MES software is powerful and dynamic, yet it needs everyone to be on board to make it effective.