Pharmaceutical manufacturers are under continuous pressure to remain competitive while meeting the stringent regulatory manufacturing requirements. These manufacturing requirements range from simple electronic record keeping to complex data assuring consistently the reliability of the manufacturing processes, equipment and people’s training, raw material quality, sampling plans, root-cause-analysis, product’s deviations, etc. Atachi Systems’ experience in deploying MES for pharmaceutical manufacturing companies for several years in a row is a testimonial on its own. Put simply, Atachi Systems understands the importance of deploying an MES system that is strategic to its core manufacturing requirements, yet cost effective to maintain and run for years to come! Our clients call it the Atachi Advantage.
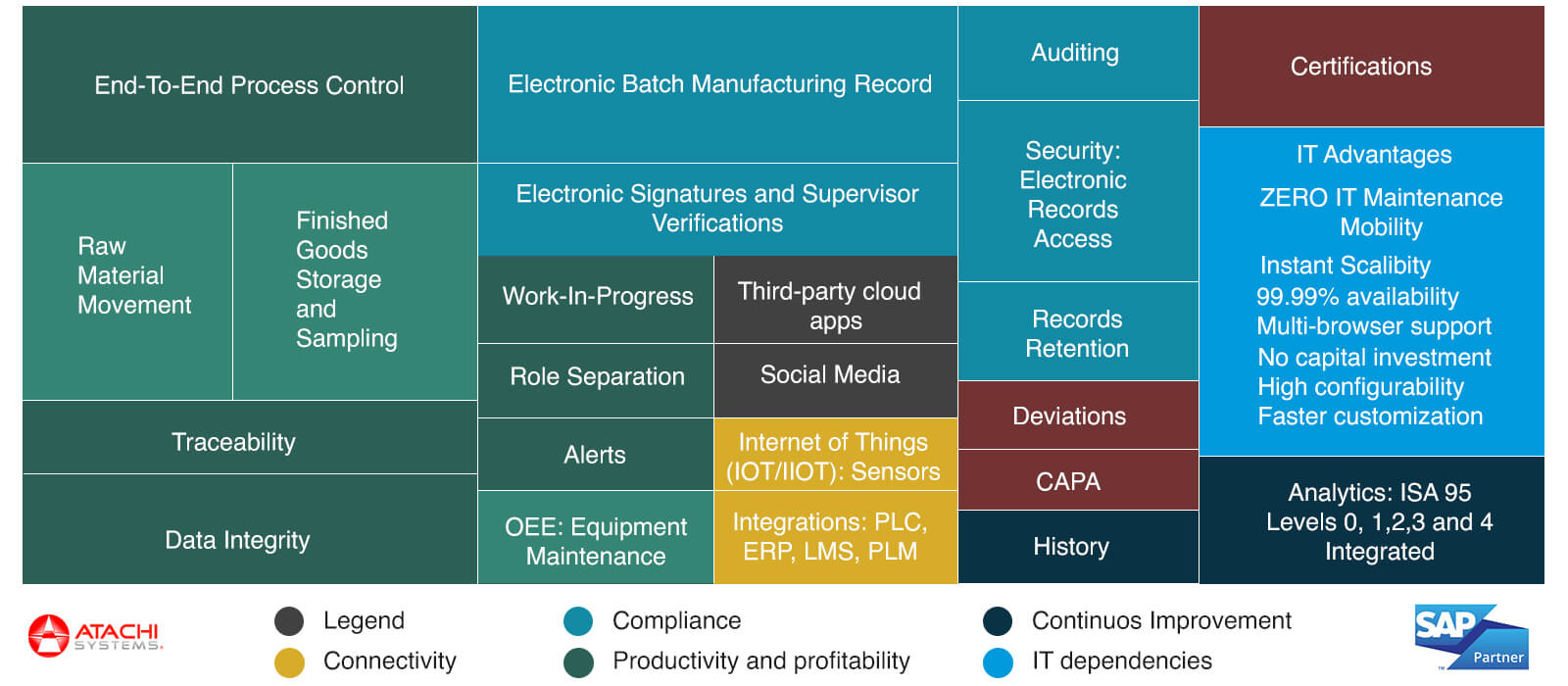
NGIMES is the “premiere” MES for pharmaceutical manufacturing companies that uses SAP ERP. It helps comply with 21CFR Part 11 electronic signatures, FDA audits, validation and confirms to US FDA cGMP requirements. Furthermore, pharmaceutical companies can take advantage of the cloud based MES (NGIMES) to contain costs while delivering accelerated performance with its in-memory computing platform. Below image covers all the MES functionalities detailed in ISA-95 model that Atachi NGIMES brings.
NGIMES
Atachi Systems has the experience and knowledge to deliver on every aspect of regulated pharmaceutical manufacturing with various MES solutions including NGIMES, a cloud-based MES solution that is run on the SAP HANA platform. Our hands-on experience working with other MES systems in the marketplace is unmatched because we understand the criticality of data migration to and from these systems to ensure total client satisfaction.
Young and fast growing Indian pharmaceutical companies have shown a keen interest in migrating to NGIMES because of its solid performance on SAP HANA and its unique industry specific pricing structure. This combined with SAP worldwide support and training makes NGIMES the obvious choice for those leading edge companies who want to stand head and shoulders above their peers.
Below is a list of the most common issues and solutions that NGMIES can deliver to any pharmaceutical or medical device company. Please note that this list is updated on a regular basis as we continuously configure NGIMES to better serve our client needs and requirements.
| Problem | Solutions |
|---|---|
| Drugs adulteration within the meaning of Section 501(a)(2)(B) of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (the FD&C Act), 21 U.S.C. 351(a)(2)(B), in that the methods used in, or the facilities or controls used for, their manufacture, processing, packing, or holding do not conform to, or are not operated or administered in conformity with, CGMP | Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) enforcing the strict conformity to the cGMP requirements to ensure that right procedures are used and enforced at every step of the manufacturing process along with the equipment cleared for the production lines. |
| Investigation of out-of-specification (OOS) laboratory test results failed to identify a root cause or provide adequate corrective actions. | The whole Batch Manufacturing Record (BMR) or electronic Batch Manufacturing Record (eBMR) data needs to be captured without compromising for the data integrity to analyze and understand the root causes of the out-of-specification products manufacturing |
| Continuous improvement of the manufacturing process | Corrective and Preventive actions need to be identified, documented and implemented |
| Reliability of the manufacturing equipment used in the process | Line clearance checks need to be strictly enforced with all the relevant information and signatures holding the accountability of the individuals. |
| Failure to establish and follow adequate written procedures describing the handling of all written and oral complaints regarding a drug product. Failure to maintain an adequate written record for each investigation conducted pursuant to 21 CFR 211.192 that included the findings of the investigation and follow-up (21 CFR 211.198(a) and (b)(2)). | Corrective and Preventive actions need to be identified, documented and implemented. |
| Mixed up drugs caused by inadequate cleaning procedures, personnel flow, equipment suitability, material flow, line segregation, inappropriate line-clearance documentation, etc. | Manufacturing Execution Systems enforcing the personnel certifications for the processes, capturing the Line clearance checks and ensure that the materials are dispensed with proper sampling activities are completed |
| Failure to establish appropriate controls over computers and related systems to assure that changes in master production and control records or other records are instituted only by authorized personnel (21 CFR 211. 68(b)). | MES, CAPA and any other shop floor systems security needs to be properly ensured so that only authorized individuals have access to the data |
| Adequate documentation to prove that the processes are designed to manufacture the product safely, documented and operators have been trained and systems are ensuring that these processes are followed. 21 CFR 211.113(b)) | Ensure that Standard Operating Procedures are backed by adequate design documentation, training and process control documentation |
| Lack of appropriate documentation for rejecting the semi-finished/finished/packaging products, etc. | Documentation of scrap/product rejection reasons. |
| Reliability of the processes, equipment used, personnel worked on the batches | Documentation of the processes performed, equipment used along with Line clearance checks and personnel certified and ensure that e-signatures are captured. Any deviations need to be captured and shall generate the triggers |
| Failure to establish and document the accuracy, sensitivity, specificity and reproducibility of test methods employed by the firm (21 C.F.R. 211.165(e)) | Ensure that the processes are closely monitored by Manufacturing Execution Systems |
| Failure to routinely calibrate, inspect, or check according to a written program designed to assure proper performance and to maintain adequate written records of calibration checks and inspections of automatic, mechanical, or electronic equipment, including computers, used in the manufacture, processing, packing, and holding of a drug product (21 C.F.R 211.68(a)). | Ensure that the Equipment are closely monitored by Manufacturing Execution Systems |
API stability for Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient Manufacturers
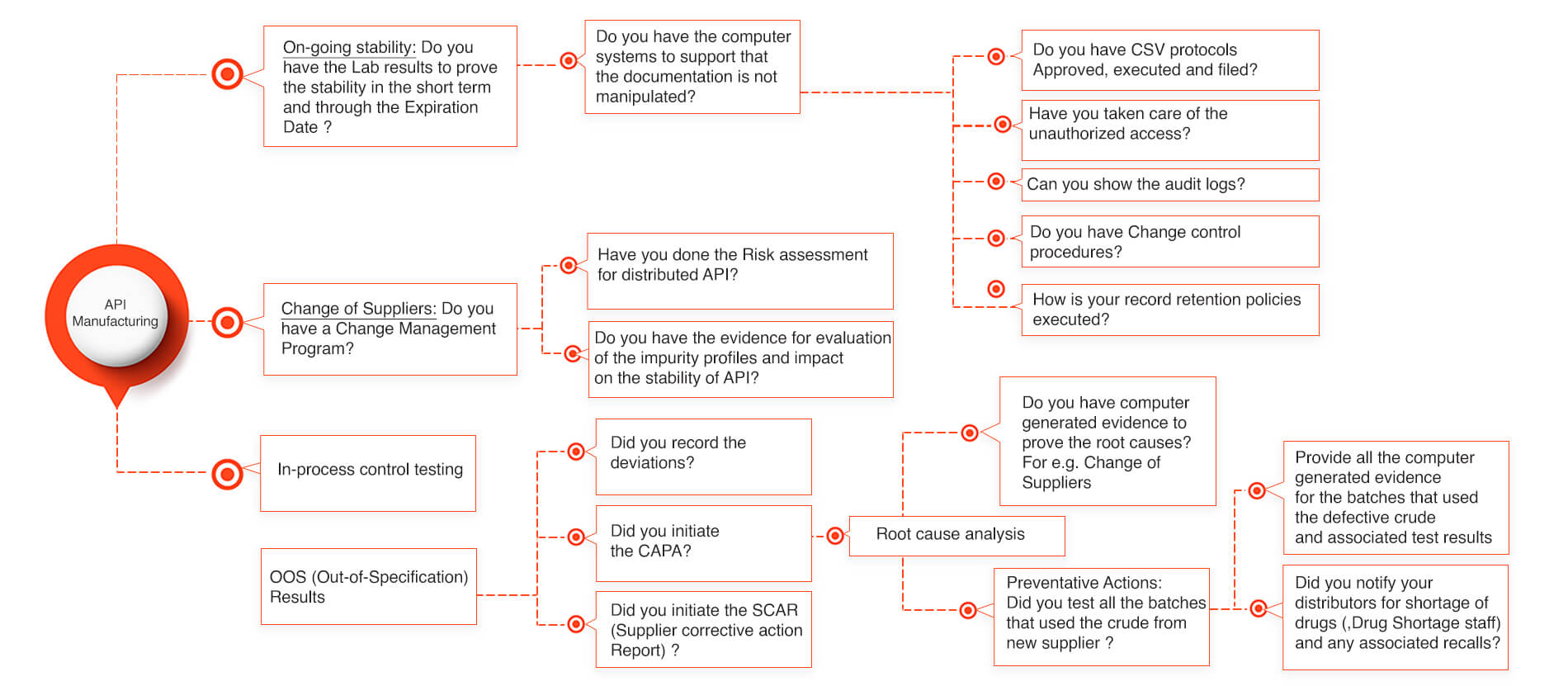
Lately few API (Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients) manufacturers have been getting the FDA warning letters for not being able to prove that their API is stable through the stability period. Lot of times the manufacturers face the critical challenges in providing the required documentation that doesn’t tie well into the data integrity of the API stability. There could be various reasons how an API stability got affected and which could have been easily prevented and saved lot of product recalls and avoided the drug shortages into the market. Our below slide gives a simplistic process that could avoid the API stability issues and reduces the FDA audit response times to as low as an hour provided the appropriate system structure is implemented.
API Stability
Data Integrity for Pharmaceutical Manufacturing companies
Data integrity has been a serious issue across all the pharmaceutical industries lately. These issues simply putting the pharmaceutical manufacturers out of the US consumer market. Put simply the impact is a growth killer for the pharma manufacturer and drug shortage for the consumer.\
It has been too expensive for small and mid-size pharma industries to own and maintain an MES systems due to the nature of the MES systems available in the market. MES systems have been built by different software companies over a period of the last 20+ years. Some of these companies have derived their roots from delivering (a) the shop floor automation solutions like PLC, DCS, SCADA integration (b) LIMS (Laboratory Information Management Systems) (c) others have come from the ERP background (d) organic MES systems providers. We have come across several world’s leading pharmaceutical manufacturers’ taking an MES road-map for a decade.
With the latest technologies the above rules are re-written with our NGIMES.
Whatever may be the dynamics of MES software market, the customers have been facing the problems with MES:
- Too expensive to own and maintain1
- Too difficult to hire and retain the talent to manage the MES2
- Too difficult to put the MES projects on right track and realize the ROI
- Too difficult to do the seamless integration of data across all the other systems on the shop-floor and present a holistic actionable intelligence to the manufacturing management.
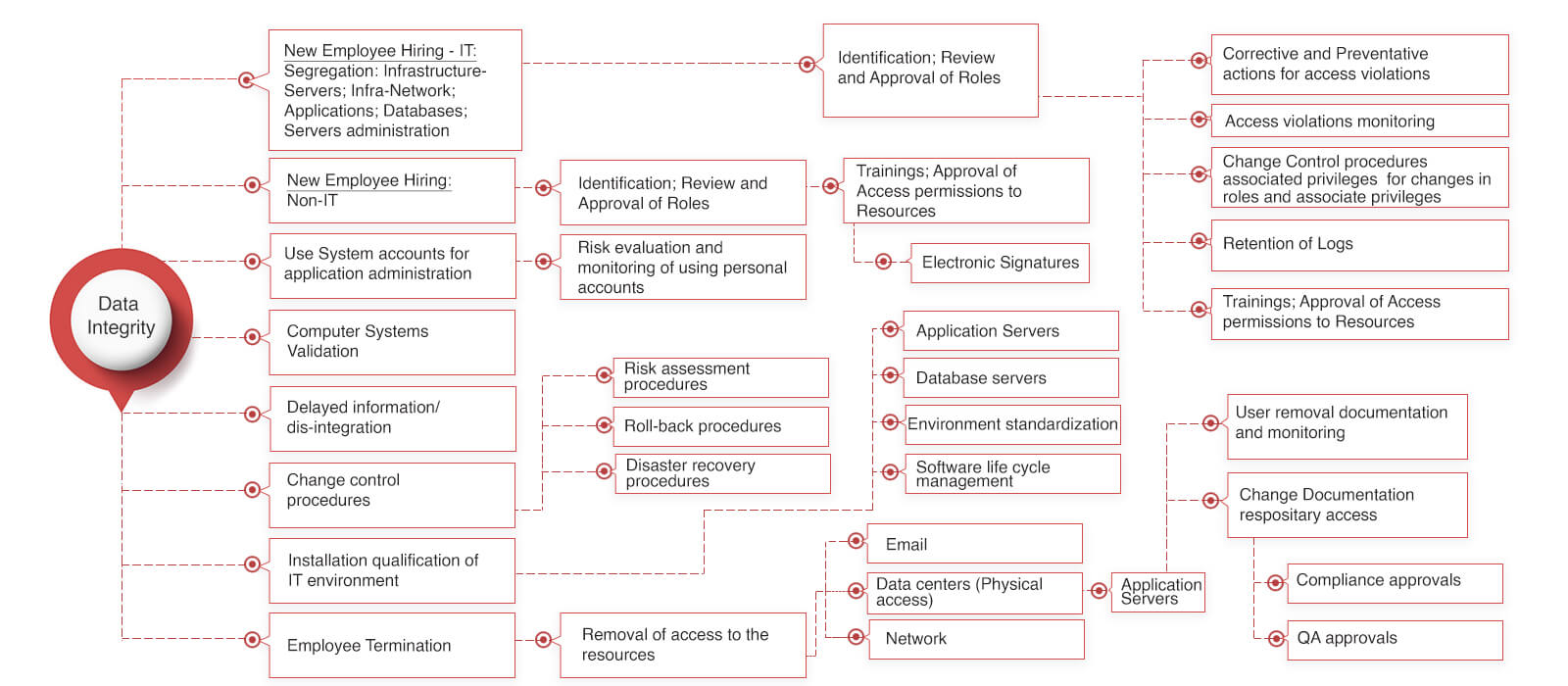
Data integrity for pharma industries issue can be well addressed with the FDA 21 CFR part 11 compliance by considering the below screen shot.
Is Data integrity killing your growth?